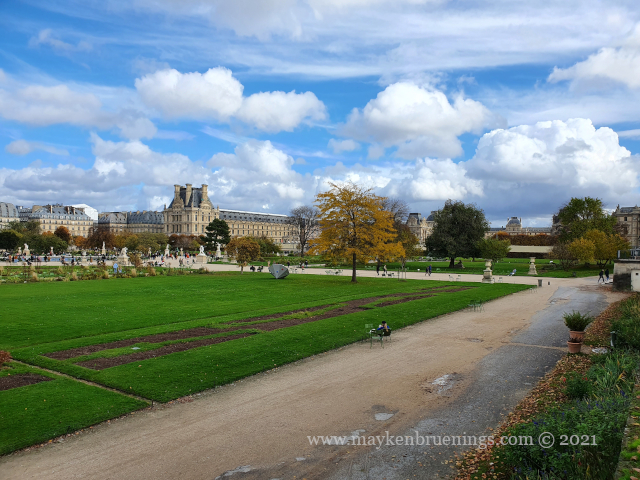
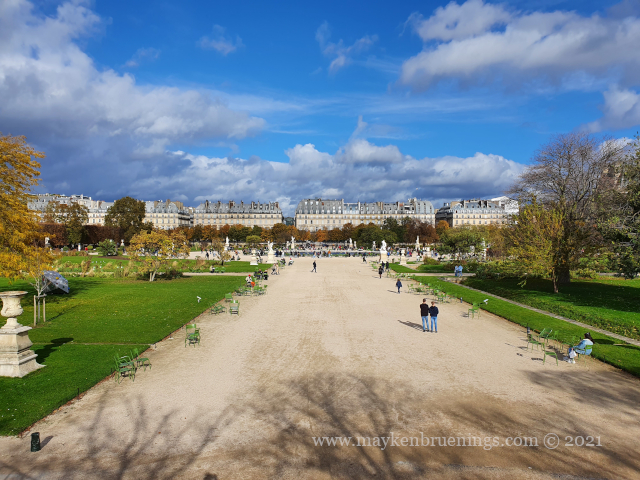
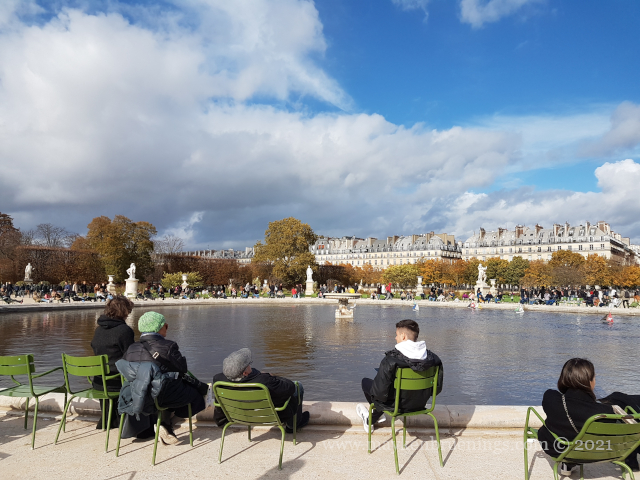
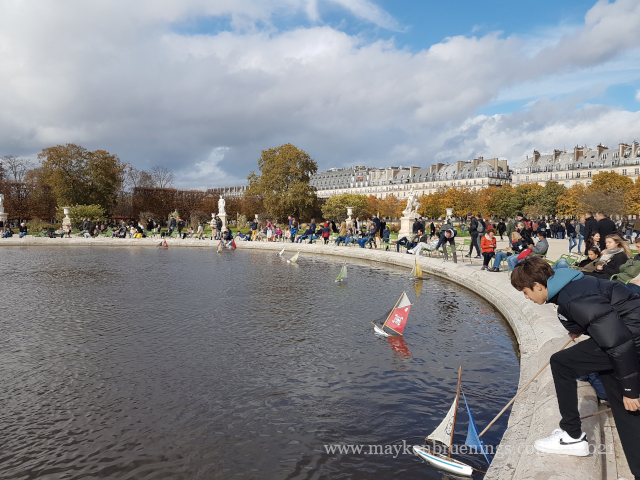
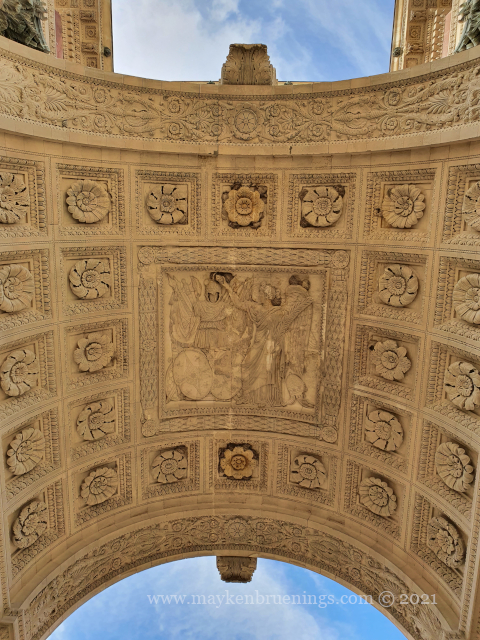
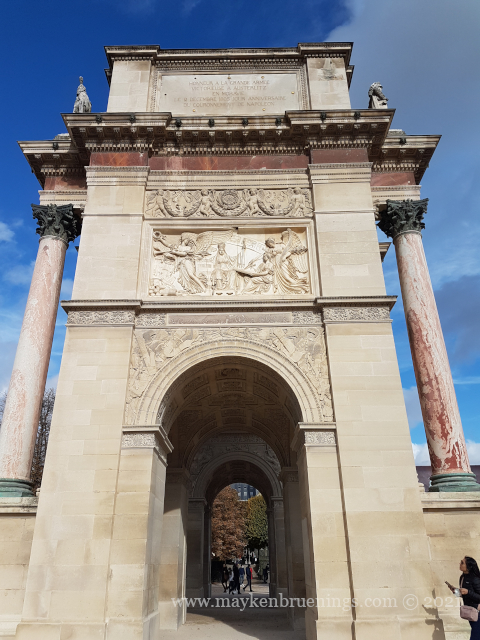
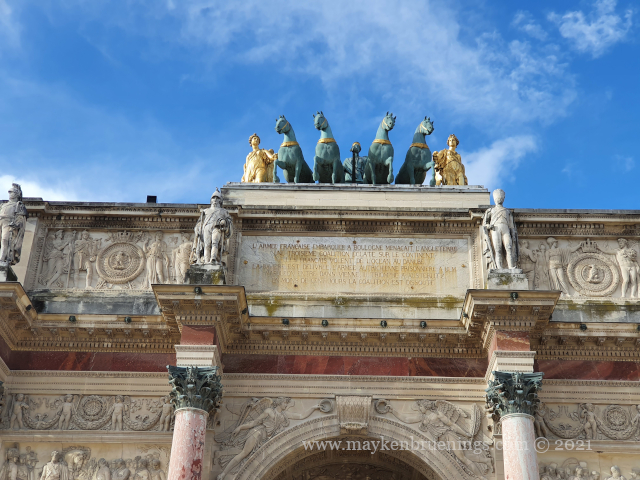
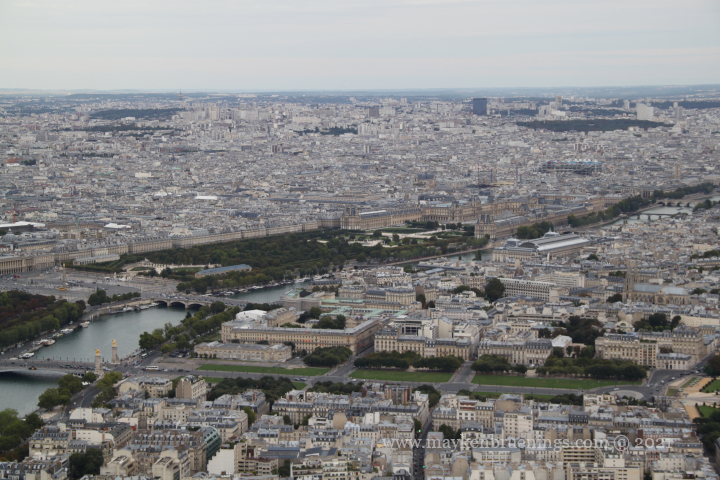
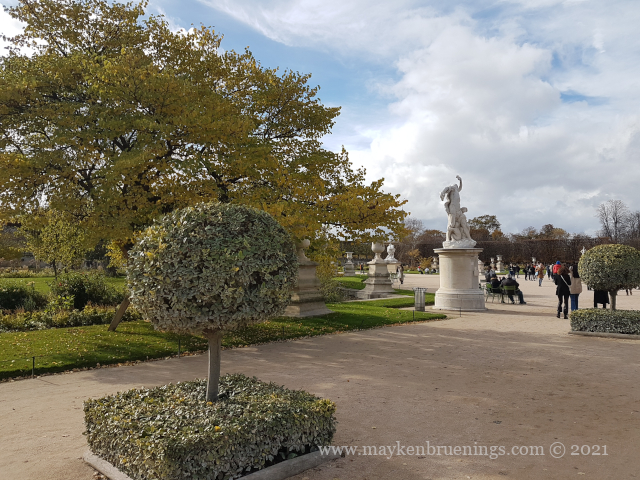
The Jardin des Tuileries is a 55 acres parc located between the Louvre and the Place de la Concorde. Its name derives from the tuileries (brickyards) that were in its place in the 13th century. Catherine de’ Medici, widow of king Henry II and mother of king François II, bought the lands which lay west of the Louvre and outside the Charles V city wall to have a new palace built with more space for gardens. Construction of the Palais des Tuileries began in 1564, and the Italian Gardens were set up on the lands between the new palace and what is today the Place de la Concorde.


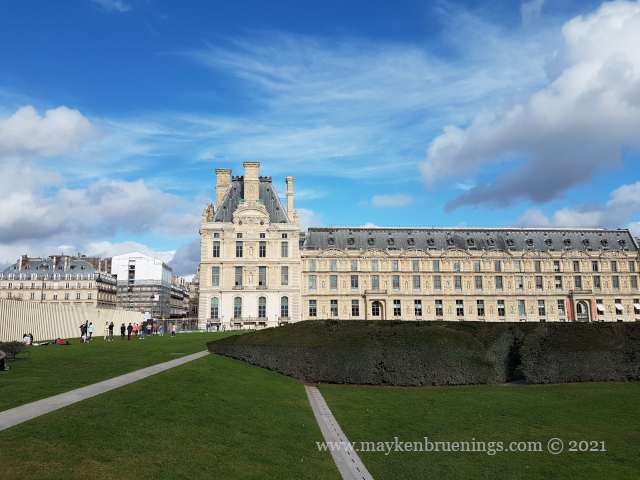
The Palais des Tuileries burnt down during the events of the Commune and its remains were demolished in 1883.

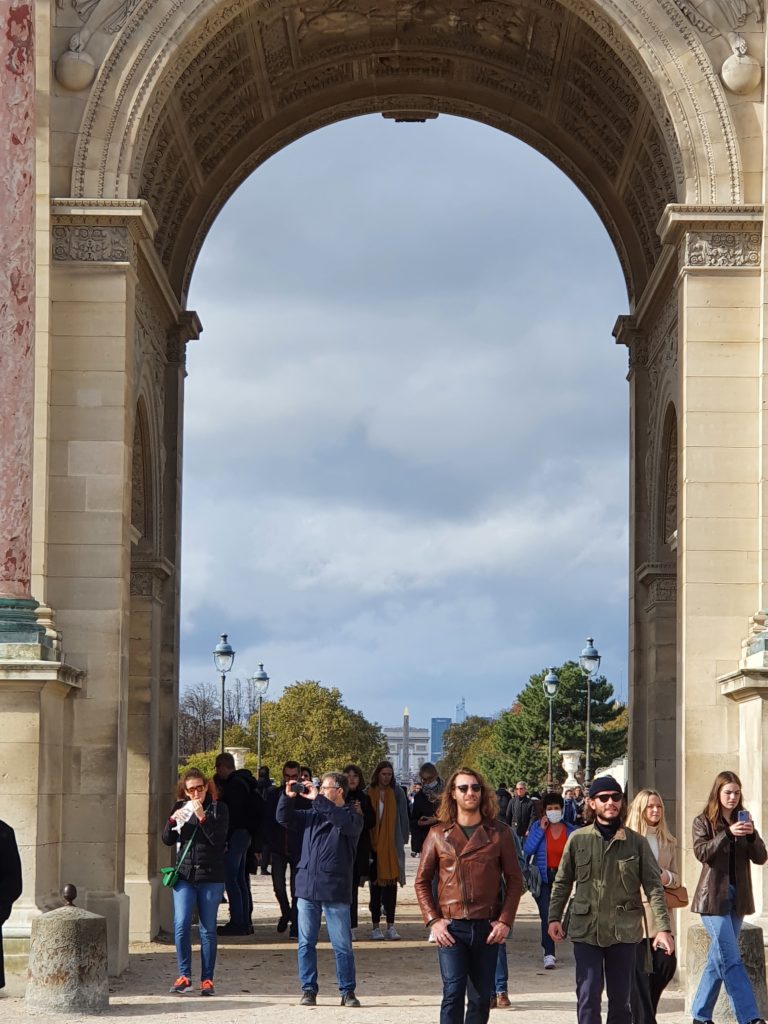
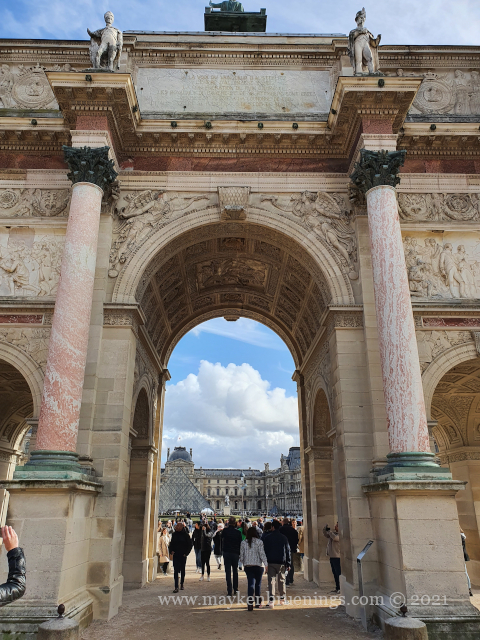
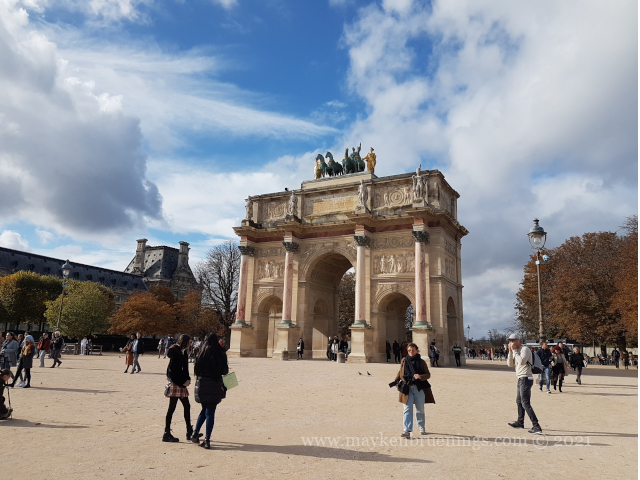
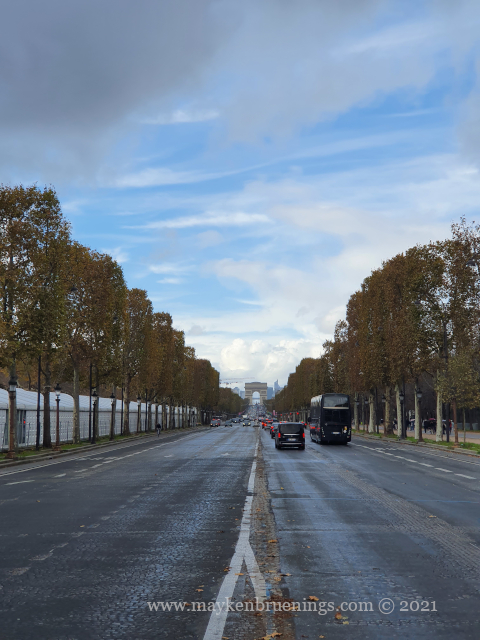
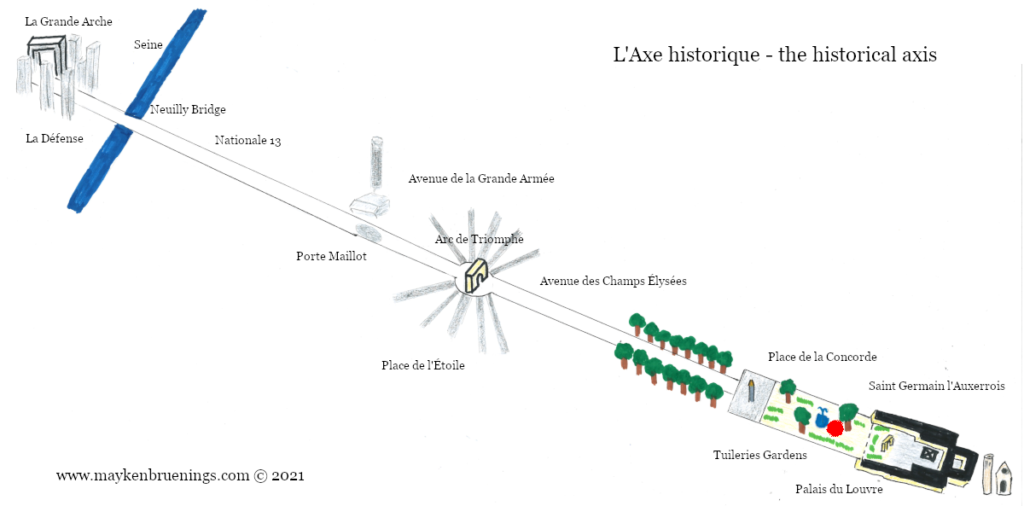
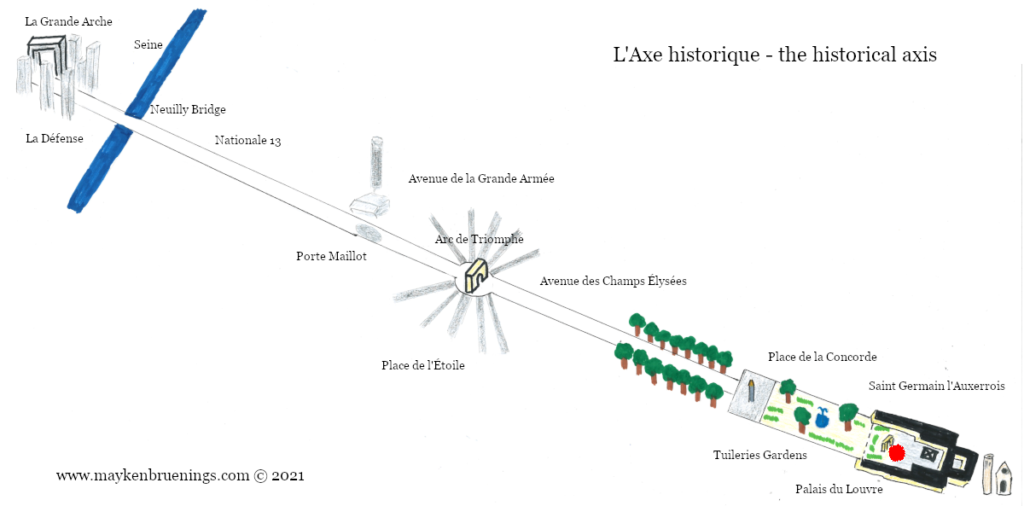
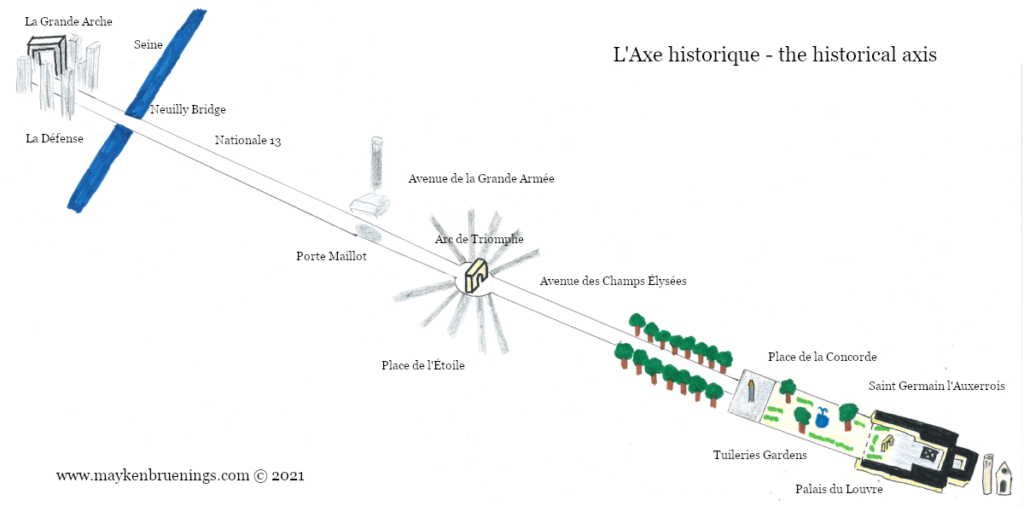
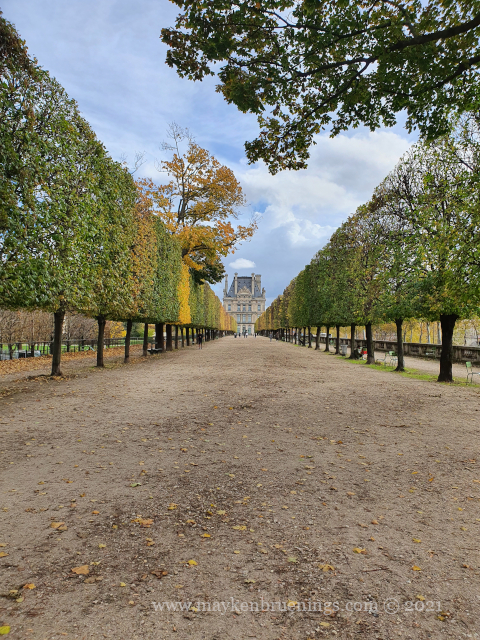
The historic axis has a slight kink at the Tuileries Palace site as you will notice if you stand at the Arc de Triomphe du Carrousel. The straight line that runs from Concorde along the Champs Élysées to the Arc de Triomphe de l’Étoile and beyond it to the Grande Arche de La Défense, was originally centered on the façade of the Tuileries Palace. The line east of the Tuileries Palace was centered on the façade of the Louvre, and since the two façades are at slightly different angles, the line in its continuation is not straight.