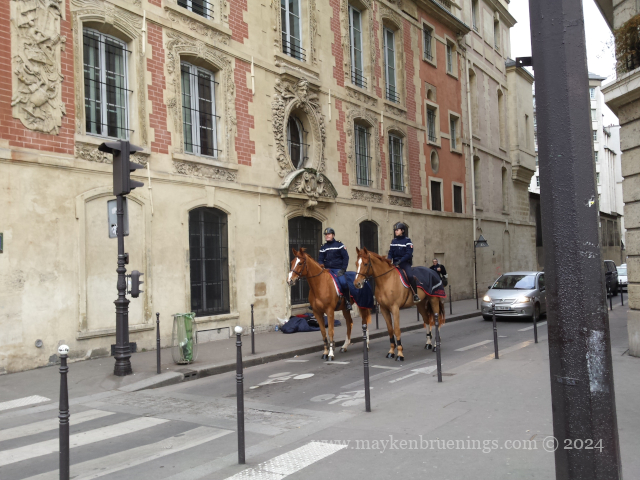
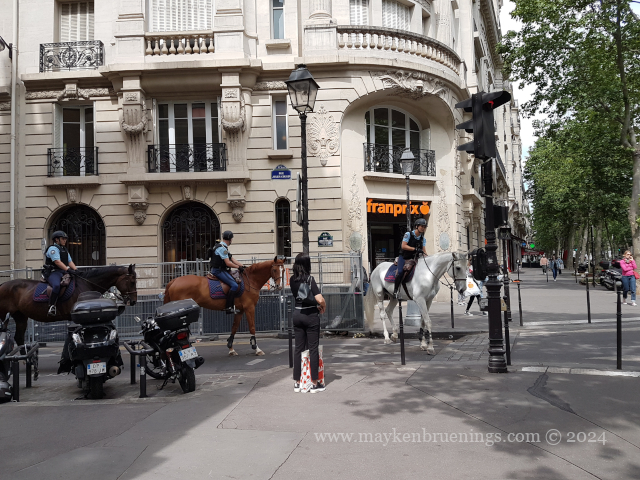
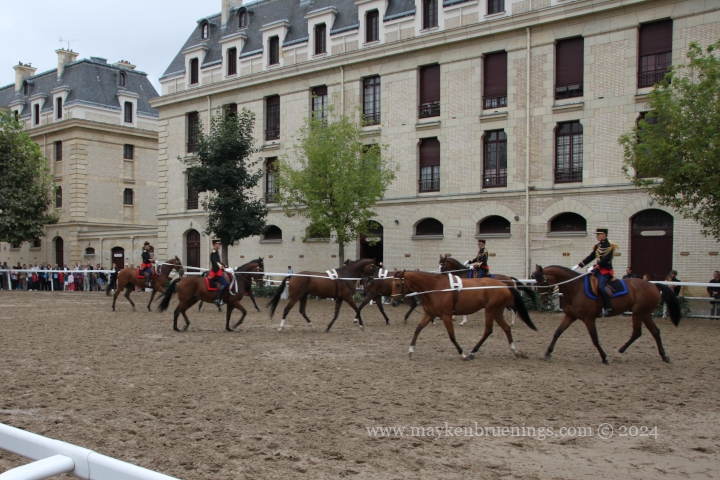
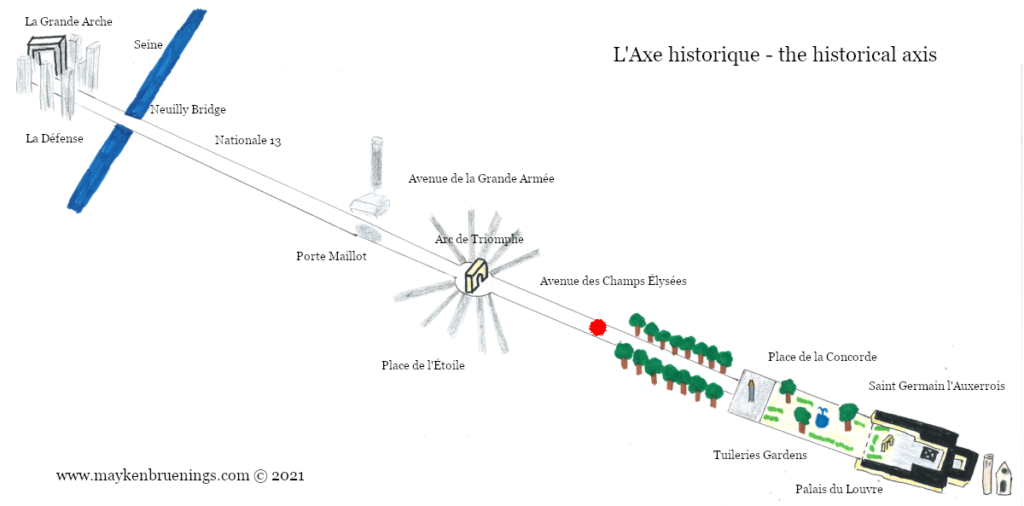
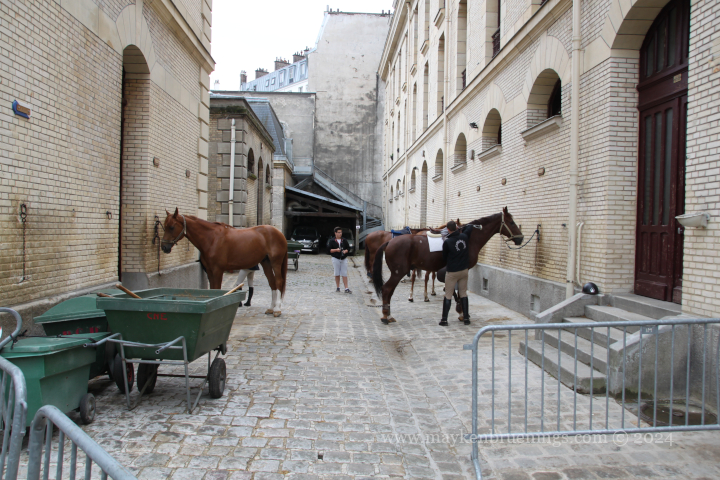Have you been in the area between the Place de la Bastille and the Seine and happened to cross riders on horseback?
Chances are you met members of the Garde Républicaine, the Republican Guard, on patrol. Yes, those same ones you see parade on July 14 on the Champs Élysées.
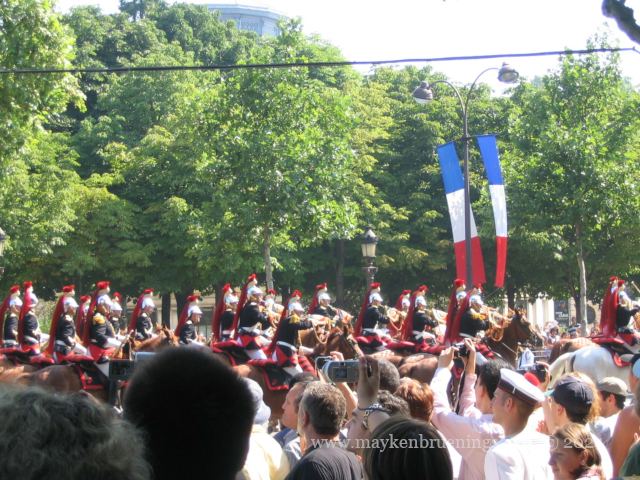

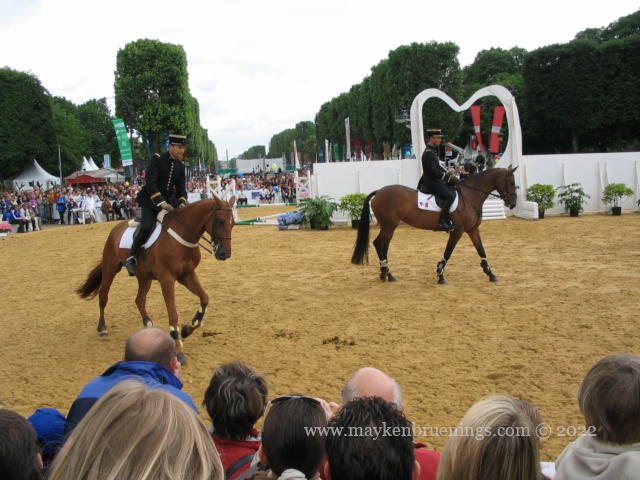
Note the traditional helmets which date back to 1876, inherited from the dragoons and cuirassiers of the First Empire.
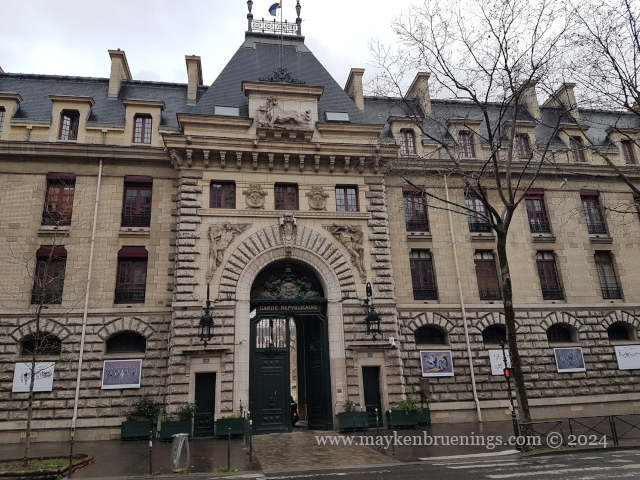
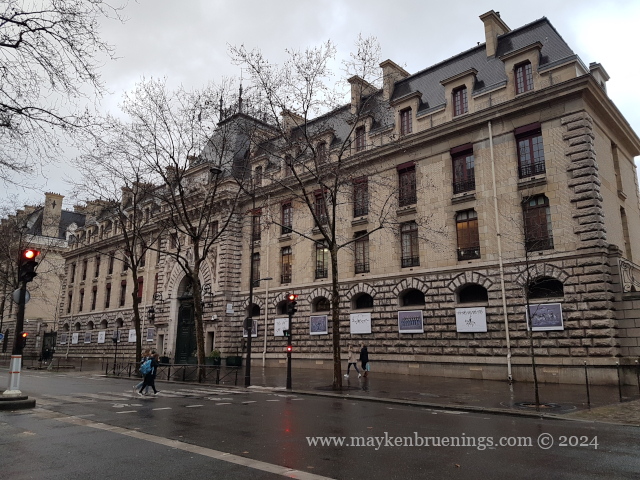
The cavalry of the Republican Guard is housed in the Célestins Quarter with its main entrance on boulevard Henri IV.
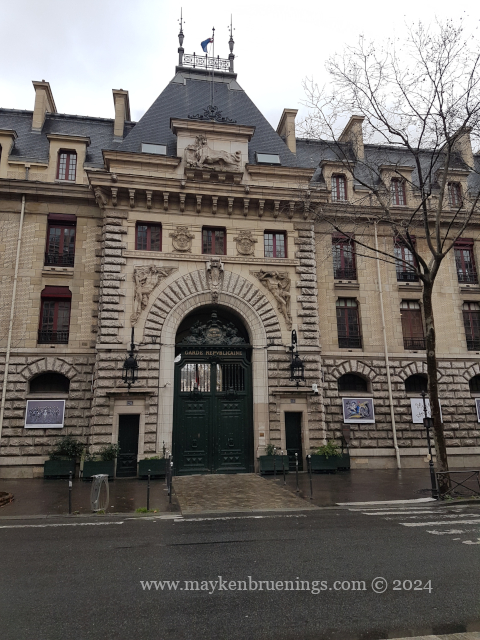

Its most visible role is in the honor missions (escorts, also carried out by the motorcycle squadron) although those represent only about 20% of the total. The majority consists of security missions such as patrols in Paris, the Bois de Boulogne and the Bois de Vincennes, but also in the forest of Chambord royal palace and other royal forests.

They also carry out surveillance of the sites at summit meetings for certain sports events and in areas with difficult access, for example a missing person search in the woods, and also surveillance of tourist areas.

The origins of the Republican Guard go back to Napoléon Ier, who created the Municipal Guard of Paris in 1802. After many back and forth over the turbulent period of the early 19th century, it was integrated into the Gendarmerie in 1849 by Napoléon III.
Contrary to other cavalry units, the Republican Guard did not participate in WWI as its mission was to maintain order in Paris and oversee the city’s defense. That is how it survived as the last mounted regiment.
During WWII, the Republican Guard was demobilized and attached to the Police Prefecture under the name of Paris Guard. Part of the troops secretly joined Charles de Gaulle, and the Guard participated with the French Forces of the Interior in the combats for the liberation of Paris.
The Guard also participated in the Indochina War from 1947 to 1954, and in 1978 it changed its name back to Republican Guard.
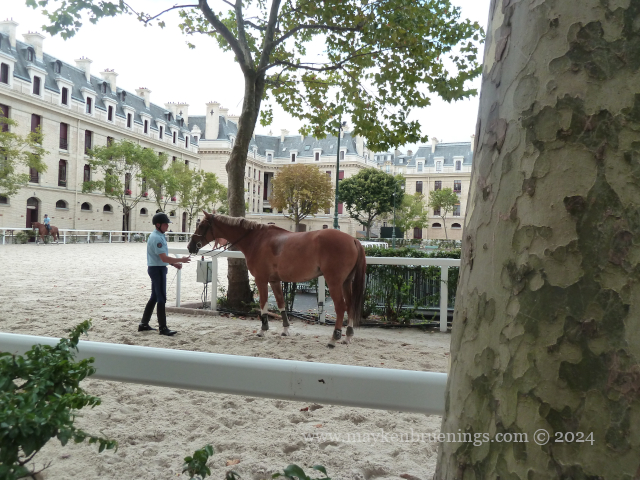

President Emmanuel Macron initiated a “horse diplomacy” by giving a Republican Guard horse to the Chinese president in 2018. He gifted another Republican Guard horse to Queen Elizabeth II for her Platinum Jubilee in 2022.
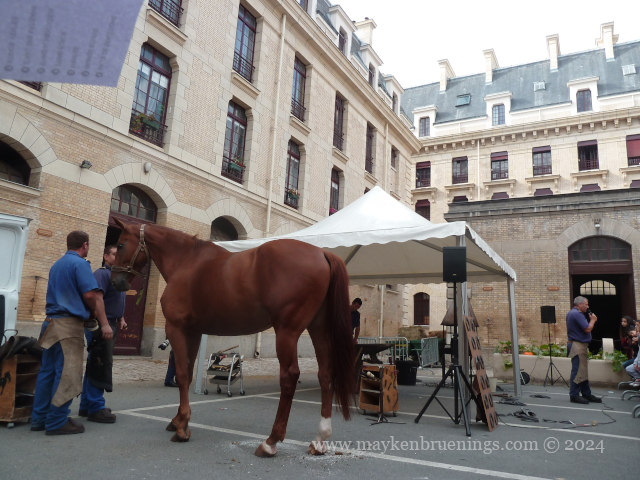
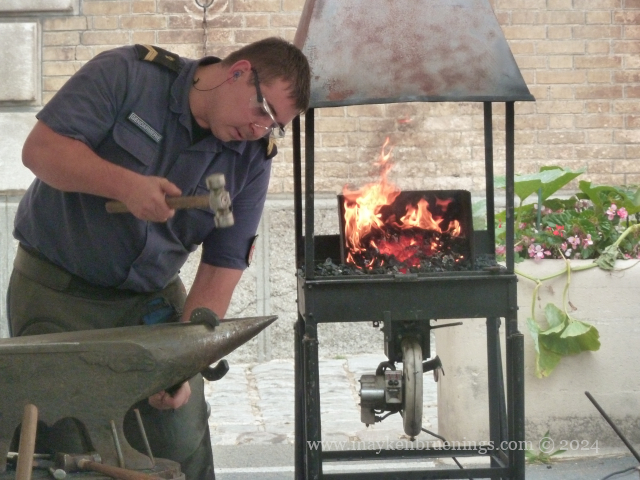
On Heritage Days in September, the Republican Guard will open the doors of the Célestins Quarter where you can see riding demonstrations, visit the horses in their stables and see the blacksmith at work.
Did you know the horseshoe sizes range from 28 to 50, with the smallest fitting inside the largest?
At the Paris International Agricultural Fair 2024, the Republican Guard, including their fanfare or orchestra, put on an impressive show. A few highlights below.